BYU Student Author: @Hyrum
Reviewers: @Mike_Paulsin, @Jonathan_Weston, @Jae
Estimated Time to Solve: 60 Minutes
We provide the solution to this challenge using:
- Python
Need a program? Click here.
Overview
You have just landed a job at a prestigious accounting firm, known for their expertise in providing financial services to high-profile clients. Your first day on the job is met with excitement and anticipation as you eagerly wait to meet your manager and learn more about the work you will be doing.
As you settle into your new role, your manager approaches you and shares with you a challenge she has been facing. She explains that creating balance sheets for clients is a time-consuming and tedious process, especially when working with a large amount of financial data. Your manager has heard about your exceptional accounting skills and proficiency in Python and believes you can help solve this problem.
She has provided you with the basic financial information for this year’s balance sheet and has asked you to create a program that will generate a balance sheet in Microsoft Word. However, she has also emphasized the need for the program to be flexible, as clients may add new assets, liabilities, or equity to the system at any time. Your manager is counting on you to use your expertise to create a solution that is both efficient and professional.
With your extensive knowledge in accounting and Python programming, you are excited to take on this challenge and deliver a high-quality product that meets your manager’s needs. You roll up your sleeves and get to work, determined to make a positive impact in your new role.
Instructions
You will need to install docx for this code. The way to do that is by running this code through your python tool:
pip install python-docx
Go ahead and copy and paste the financial data into whatever python tool you have. Here is the financial data for this year and last year:
Financial Data
#accounts and balances for this year
assets = {'Cash': 1000,
'Accounts Receivable': 5000,
'Inventory': 2500,
'Equipment': 10000}
liabilities = {'Accounts Payable': 2000,
'Notes Payable': 5000}
equity = {'Retained Earnings': 6500,
'Common Stock': 5000}
#accounts and balances for last year
assets_last_year = {'Cash': 1000,
'Accounts Receivable': 3500,
'Inventory': 1500,
'Equipment': 8000}
liabilities_last_year = {'Accounts Payable': 1500,
'Notes Payable': 2000}
equity_last_year = {'Retained Earnings': 5500,
'Common Stock': 5000}
Copy and paste the above code into a code of whatever python tool you use. You can assume that the system you would use your python code with would automatically supply dictionaries like the one above.
Write a python Script that does the following:
- Calculates total assets and total Liabilities & Equity. Calculate for both this year and last year
- Format the code onto a word document
- Make the code flexible enough so that if more assets, liabilities, or equity are added to the associated dictionaries, then your code will still work.
Suggestions and Hints
Here is a resource to use if you are not familiar with docx:
Create Table in Word DOCX in Python | Create Nested Tables in Python
- To start, make a document using the following code:
doc = doc.add_table(rows=#of rows wanted, cols=#of columns wanted) - To add a table:
doc.add_table(rows, columns) - To add a new row:
table.add_row().cells - Use “.2f” to format into currency
- Use a for loop through the dictionaries and stay adaptable
This is what the final table should look like:
Balance sheet
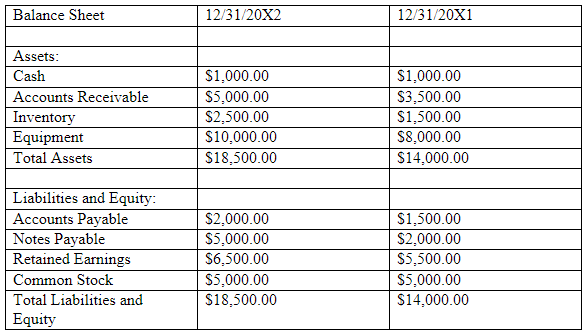
Solution
Solution Code
import docx
# Step 1: Define the accounts and balances for this year
assets = {'Cash': 1000,
'Accounts Receivable': 5000,
'Inventory': 2500,
'Equipment': 10000}
liabilities = {'Accounts Payable': 2000,
'Notes Payable': 5000}
equity = {'Retained Earnings': 6500,
'Common Stock': 5000}
# Step 2: Calculate the total assets for this year
total_assets = sum(assets.values())
# Step 3: Calculate the total liabilities for this year
total_liabilities = sum(liabilities.values())
# Step 4: Calculate the total equity for this year
total_equity = sum(equity.values())
# Step 5: Calculate the total liabilities and equity for this year
total_liabilities_equity = total_liabilities + total_equity
# Step 6: Define the accounts and balances for last year
assets_last_year = {'Cash': 1000,
'Accounts Receivable': 3500,
'Inventory': 1500,
'Equipment': 8000}
liabilities_last_year = {'Accounts Payable': 1500,
'Notes Payable': 2000}
equity_last_year = {'Retained Earnings': 5500,
'Common Stock': 5000}
# Step 7: Calculate the total assets for last year
total_assets_last_year = sum(assets_last_year.values())
# Step 8: Calculate the total liabilities for last year
total_liabilities_last_year = sum(liabilities_last_year.values())
# Step 9: Calculate the total equity for last year
total_equity_last_year = sum(equity_last_year.values())
# Step 10: Calculate the total liabilities and equity for last year
total_liabilities_equity_last_year = total_liabilities_last_year + total_equity_last_year
# Step 11: Create a new Word document
doc = docx.Document()
# Step 12: Add the Balance Sheet table to the document
table = doc.add_table(rows=1, cols=3)
table.style = 'Table Grid'
table.cell(0, 0).text = 'Balance Sheet'
table.cell(0, 1).text = '12/31/20X2'
table.cell(0, 2).text = '12/31/20X1'
row_cells = table.add_row().cells
row_cells[0].text = ''
row_cells[1].text = ''
row_cells[2].text = ''
row_cells = table.add_row().cells
row_cells[0].text = 'Assets:'
row_cells[1].text = ''
row_cells[2].text = ''
# Iterate through the assets and add balances for each asset listed
for account, balance in assets.items():
row_cells = table.add_row().cells
row_cells[0].text = account
row_cells[1].text = f'${format(balance, ",.2f")}'
row_cells[2].text = f'${format(assets_last_year[account], ",.2f")}' if account in assets_last_year else '-'
# Add Total Assets
row_cells = table.add_row().cells
row_cells[0].text = account = 'Total Assets'
row_cells[1].text = f'${format(total_assets, ",.2f")}'
row_cells[2].text = f'${format(total_assets_last_year, ",.2f")}'
row_cells = table.add_row().cells
row_cells[0].text = ''
row_cells[1].text = ''
row_cells[2].text = ''
# Caption total Liabilities and Equity
row_cells = table.add_row().cells
row_cells[0].text = 'Liabilities and Equity:'
row_cells[1].text = ''
row_cells[2].text = ''
# Iterate through each of the liabilities and add balances for each one
for account, balance in liabilities.items():
row_cells = table.add_row().cells
row_cells[0].text = account
row_cells[1].text = f'${format(balance, ",.2f")}'
row_cells[2].text = f'${format(liabilities_last_year[account], ",.2f")}' if account in liabilities_last_year else '-'
# Iterate through each of the equity accounts and add balances for each one
for account, balance in equity.items():
row_cells = table.add_row().cells
row_cells[0].text = account
row_cells[1].text = f'${format(balance, ",.2f")}'
row_cells[2].text = f'${format(equity_last_year[account], ",.2f")}' if account in equity_last_year else '-'
# Add total Liabilities and Equity
row_cells = table.add_row().cells
row_cells[0].text = 'Total Liabilities and Equity'
row_cells[1].text = f'${format(total_liabilities_equity, ",.2f")}'
row_cells[2].text = f'${format(total_liabilities_equity_last_year, ",.2f")}'
# Step 8: Save the Word document
doc.save('balance_sheet.docx')
Solution Video: Challenge 80|PYTHON – Financial Formatting
